Basic concepts
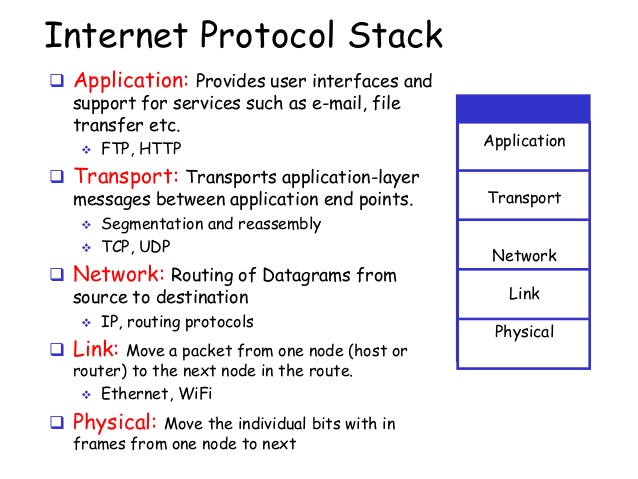
- TCP/IP model layers
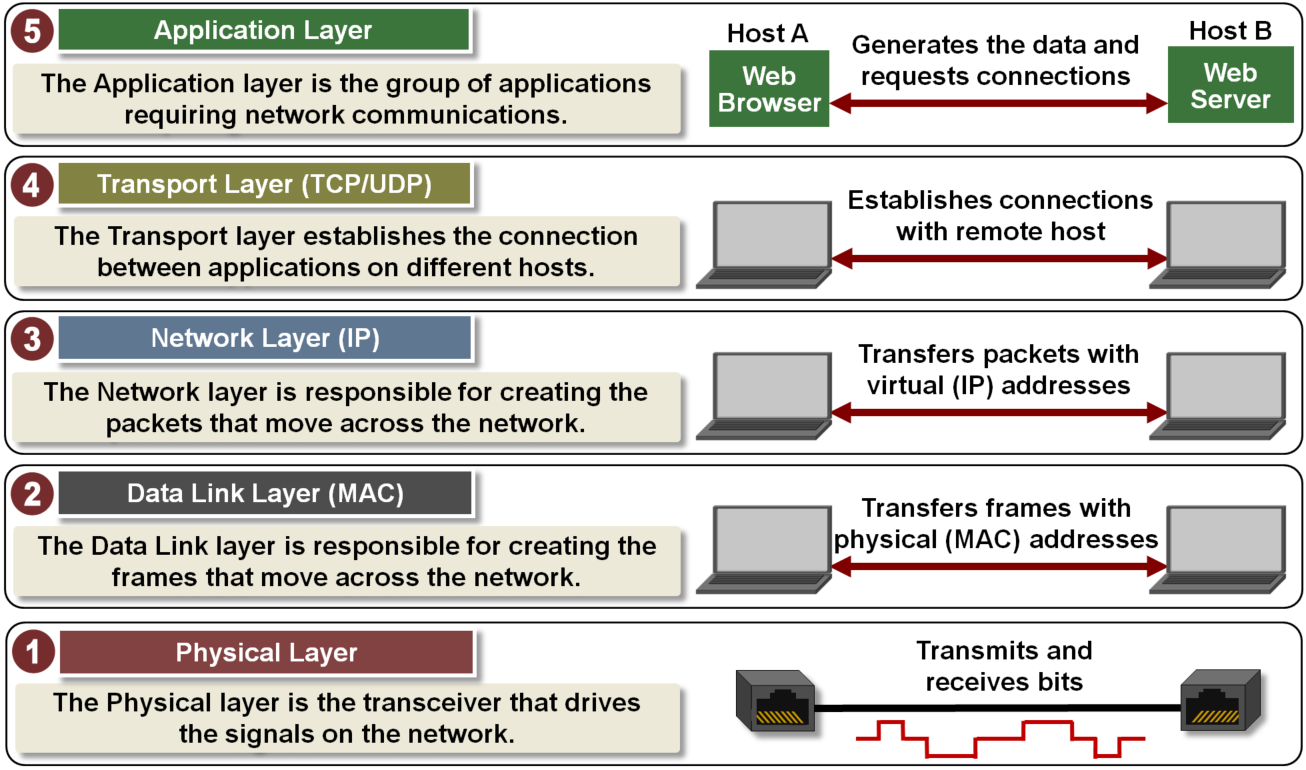
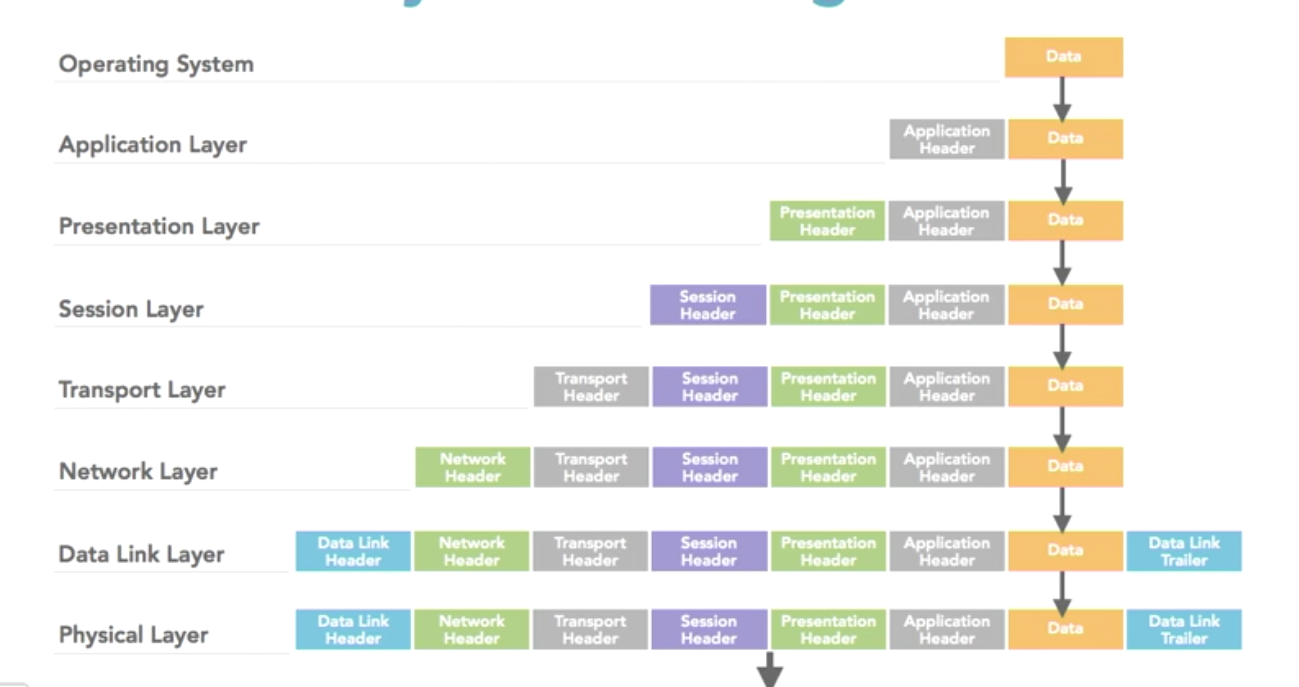
- Add header from the higher leyer to the lower layer
- Process of data transmission
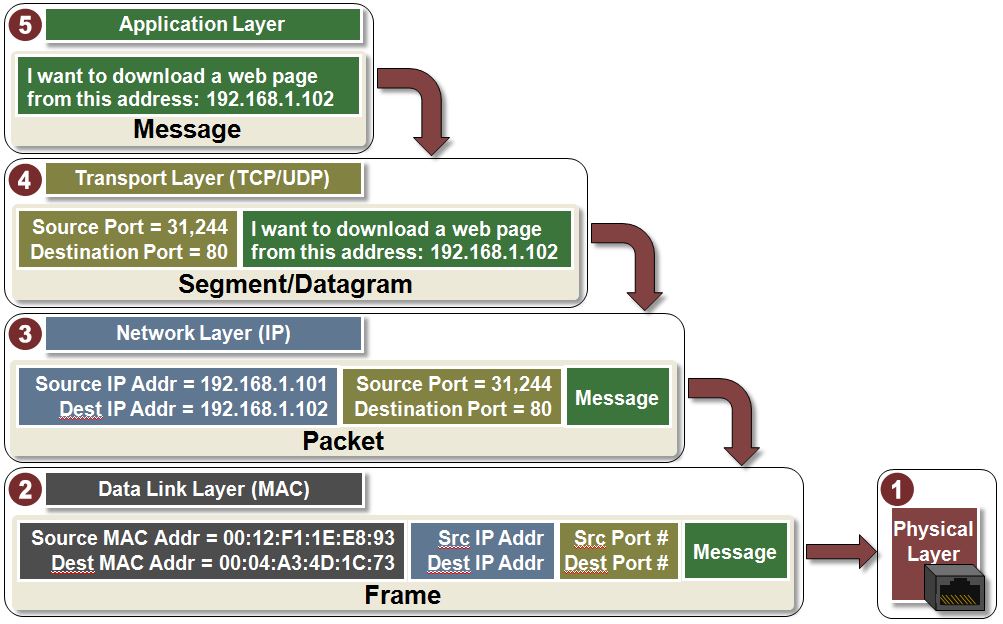
- From higher layer to lower laryer in sender, From lower layer to higher layer in receiver
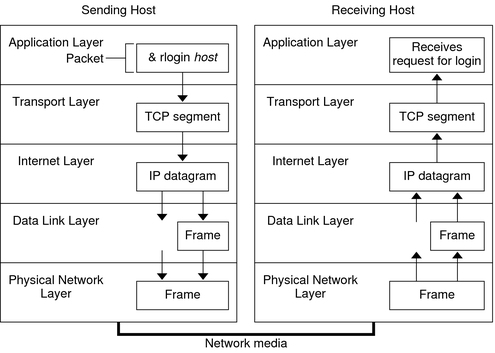
- Client: sends/requests data to server
- A single machine can be both client and server at the same time. eg. A single machine could acts as a aserver for end users and client for a database.
-
Server: returns data/service to the client, listening for incoming network calls
-
port: 16,000 ports in one machine eg HTTP 80, HTTPS 443 port#
- IP address: Address that each machine connected to the public Internet. a.b.c.d (four numbers are all (0, 255))
- 127.0.0.1 is to localhost, 192.168.a.b is to private network, have 192.168 prefix, internal network.
- IP: Internet protocal, IP address. IP packet: stored in bytes
-
IP header:
source IP address, destination address, total size of packet, internet IP version IPV4 or IPV6 Payload: data to send(2^16 bytes) so we need multiple ip packets (TCP) for large files
-
- TCP: transmission control protocal. Send IP packet in order. Error free way, resend if incorrect. Build on top of IP.
- Allow for ordered, reliable data delivery between machines over the public internet by connection.
-
TCP structure:
IP header TCP header data - TCP connection, handshake, timed out, end the connection, sockets to applications
- HTTP: HeperText transfer protocol. request-response paradigm. More business logical than IP and TCP. Build on top of TCP.
- http request: host, port, method(get, put, post, delete), path, headers, body, cookie
- http responces: statusCode, headers, body
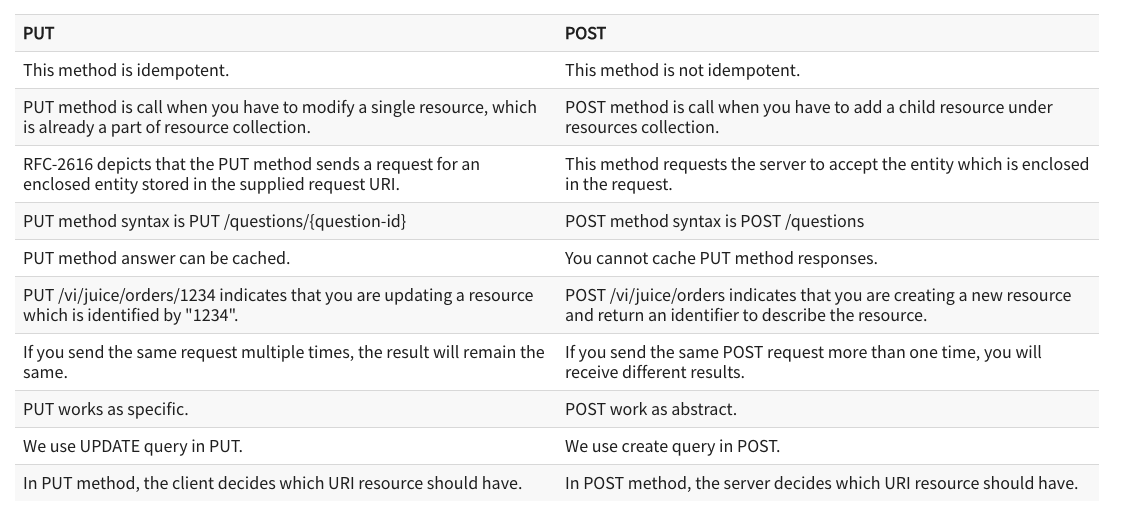
- Difference between POST and PUT?
Try examples
Mock client and server
Send data to local machine port
nc 127.0.0.1 8081(terminal1) Listen data from local machihe portnc -l 8081(terminal1) You can send data from the first terminal
Find IP address of a public url
find IP address in Mac
dig google.com
Send/retrive data to servers
curl localhost:8080/worlddefault http, get
What happened when you enter an url to your browser
browser(client) -> DNS query(IP address) -> send HTTP request(IP packet) -> Google.com(server) -> reponse HTML/CSS to clients
- Initial typing: auto complement, history and local cache
- Url parsing: url or search words
-
Find protocol: HTTPS 443 (default) or HTTP 80
- DNS lookup (domain name server): IP address, local cache or DNS over HTTPS
- DNS is UDP server, send packet, send to router via to NAT gateway, get response from ISP(Internet Service Provider ) of IP address of google.com
- TCP connection: 3 way handshake to build connection, go through many routers
- Client Hello, server Hello, TLS protocol, Client key exchange, Server key exchange
- GET request: Cookie together with the get request, send the header, response with the HTML web page body
- http request: host, port, method(get, put, post, delete), path, headers, body, cookie
- passowrd and username: token, store in cookie. Check whether is the correct person to log in.
- http responces: statusCode, headers, body
- HTML parsing: content-type html, image, html, js, css